View的滑动
View的位置主要由它的四个顶点来决定,分别对应于View的四个属性:top,left,right,bottom,其中top是左上角的纵坐标,left是左上角的横坐标,right是右下角的横坐标,bottom是右下角的纵坐标。需要注意的是,这些坐标都是相当于View的父容器来说的,因此它是一种相对坐标,View的坐标和父容器的关系如下所示: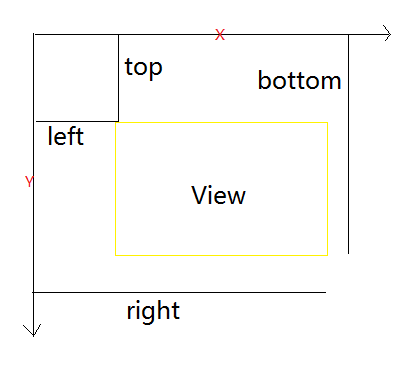
width = right - left
height = bottom - top
left = getLeft()
right = getRight()
top = getTop()
bottom = getBottom()
从Android3.0 开始,View增加了额外的几个参数:x,y,trabslationX和translationY。其中x和y是View左上角的坐标,而translationX和translationY是View左上角相对于父容器的偏移量。这几个参数也是相对于父容器的坐标,并且translationX和translationY的默认值是0,和View的四个基本的位置参数一样,View也为他们提供了get/set方法,这几个参数的换算关系如下x = left + translationX
需要注意的是,View在平移过程中,top和left表示的是原始左上角的位置信息,其值并不会发生改变,此时发生改变的是x,y,translationX和translationY。
一 VelocityTracker 和 GestureDetector
速度最终,用于追踪手指在滑动过程中的速度,包括水平和竖直方向的速度。使用方法在View的onTouchEvent方法中追踪当前单击事件的速度:
1 | |
接着,当我们想知道当前的滑动速度时,这个时候可以采用如下方式来获得当前速度:
1 | |
在这一步中有两点需要注意
- 获取速度之前必须先计算速度,即getXVelocity()和getYVelocity()之前必须调用computeCurrentVelocity(1000)
- 这里的速度时指一段时间内手指所划过的像素数,速度可以是负数,当手指在水平方向从左向右滑动时,速度为正,反之为负数。
最后,当不在使用它的时候,需要调用clear方法来重置并回收内存:1
2velocityTracker.clear();
velocityTracker.recycle();
手势检测,用于辅助检测用户的单击、滑动、长按、双击等行为。
首先创建GestureDetector的对象,接着接管View的onTouchEvent方法。做完下面两部,就可以有选择的实现接口中的方法了
1 | |
其中gestureDetector.setIsLongpressEnabled(false)是为了解决长按之后无法拖动的现象。
二 使用ScrollTo/ScrollBy
调用方式 View.scrollTo(int x, int y),View.scrollBy(int x, int y)
方法源码:
1 | |
从源码中可以看出,scrollBy实际上也是调用scrollBy的方法。需要注意的是在View的滑动过程中,mScrollX和mScrollY的改变规则:
在滑动过程中,mScrollX的值总是等于View左边缘和View内容左边缘在水平方向的距离,而mScrollY的值总是等于View上边缘和View内容上边缘在竖直方向的距离。其中mScrollX和mScrollY的单位是像素,并且当View左边缘在View内容左边缘的右边时,mScrollX为正值,反之为负值;当View上边缘在View内容上边缘的下边时,mScrollY为正值,反之为负值。换句话说:从左向右滑动,mScrollX为负值,反之为正值;如果从上往下滑动,mScrollY为负值,反之为正值。
意思就是说ScrollTo/ScrollBy只能滑动View的内容而不能滑动View本身,比如,只能滑动TextView的文字,而不能滑动TextView控件本身
三 使用动画
这个没什么好介绍的,想要兼容3.0以下的属性动画,建议使用nineoldandroids来实现
四 改变布局参数
改变布局参数,也就是改变·LayoutParams·
五 使用Scroller进行平滑移动
自定义一个控件,添加成员变量·Scroller·,如下:
1 | |
其实Scroller也是通过ScrollTO/ScrollBy实现的,同样只能滑动内容,不能滑动本身。
PS:
在调用startScroll时,并没有让View进行滑动。而是在调用invalidate()进行重绘的时候,会去调用computeScroll方法,但是computeScroll在View只是个空实现,因此需要我们自己去实现。在computeScroll中进行平移。也就是说当View重绘后在draw方法中调用computeScroll,而computeScroll又会去向Scroller获取当前的scrollX和scrollY,然后通过scrollTo方法实现滑动,接着又调用postInvalidate()方法来进行第二次重绘,这一次重绘过程和第一次一样,还是会去调用computeScroll()方法,如此反复,直到整个滑动过程结束。
以上